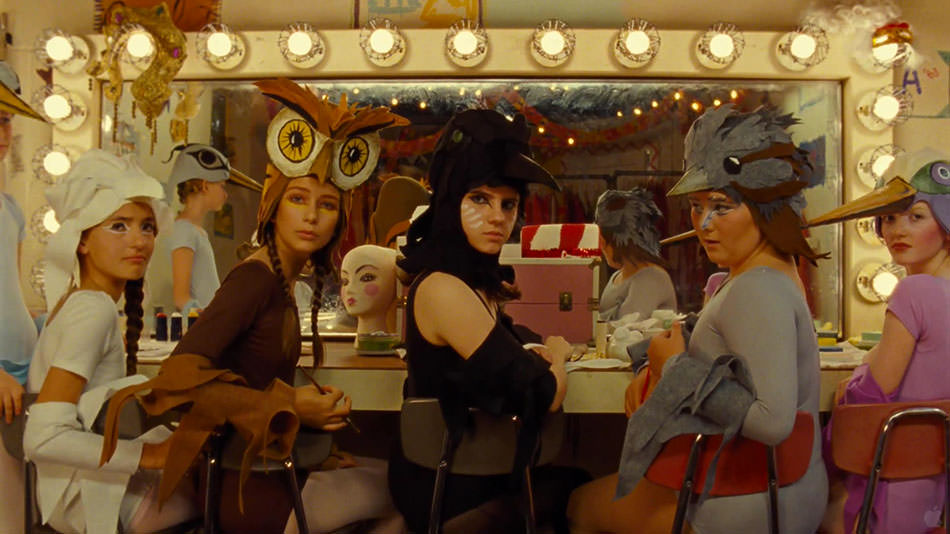The world is so big, so complicated, so replete with marvels and surprises that it takes years for most people to begin to notice that it is, also, irretrievably broken. We call this period of research “childhood.”
There follows a program of renewed inquiry, often involuntary, into the nature and effects of mortality, entropy, heartbreak, violence, failure, cowardice, duplicity, cruelty, and grief; the researcher learns their histories, and their bitter lessons, by heart. Along the way, he or she discovers that the world has been broken for as long as anyone can remember, and struggles to reconcile this fact with the ache of cosmic nostalgia that arises, from time to time, in the researcher’s heart: an intimation of vanished glory, of lost wholeness, a memory of the world unbroken. We call the moment at which this ache first arises “adolescence.” The feeling haunts people all their lives.
Everyone, sooner or later, gets a thorough schooling in brokenness. The question becomes: What to do with the pieces? Some people hunker down atop the local pile of ruins and make do, Bedouin tending their goats in the shade of shattered giants. Others set about breaking what remains of the world into bits ever smaller and more jagged, kicking through the rubble like kids running through piles of leaves. And some people, passing among the scattered pieces of that great overturned jigsaw puzzle, start to pick up a piece here, a piece there, with a vague yet irresistible notion that perhaps something might be done about putting the thing back together again.
Two difficulties with this latter scheme at once present themselves. First of all, we have only ever glimpsed, as if through half-closed lids, the picture on the lid of the jigsaw puzzle box. Second, no matter how diligent we have been about picking up pieces along the way, we will never have anywhere near enough of them to finish the job. The most we can hope to accomplish with our handful of salvaged bits—the bittersweet harvest of observation and experience—is to build a little world of our own. A scale model of that mysterious original, unbroken, half—remembered. Of course the worlds we build out of our store of fragments can be only approximations, partial and inaccurate. As representations of the vanished whole that haunts us, they must be accounted failures. And yet in that very failure, in their gaps and inaccuracies, they may yet be faithful maps, accurate scale models, of this beautiful and broken world. We call these scale models “works of art.”
From Rushmore to Moonrise Kingdom (shamefully neglected by this year’s Academy voters), Wes Anderson’s films readily, even eagerly, concede the “miniature” quality of the worlds he builds, in their set design and camera-work, in their use of stop-motion, maps, and models. And yet these miniatures span continents and decades. They comprise crime, adultery, brutality, suicide, the death of a parent, the drowning of a child, moments of profound joy and transcendence.
Vladimir Nabokov, his life cleaved by exile, created a miniature version of the homeland he would never see again and tucked it, with a jeweler’s precision, into the housing of John Shade’s miniature epic of family sorrow. Anderson—who has suggested that the breakup of his parents’ marriage was a defining experience of his life—adopts a Nabokovian procedure with the families or quasi families at the heart of all his films, from Rushmore forward, creating a series of scale-model households that, like the Zemblas and Estotilands and other lost “kingdoms by the sea” in Nabokov, intensify our experience of brokenness and loss by compressing them. That is the paradoxical power of the scale model; a child holding a globe has a more direct, more intuitive grasp of the earth’s scope and variety, of its local vastness and its cosmic tininess, than a man who spends a year in circumnavigation.
Grief, at full scale, is too big for us to take it in; it literally cannot be comprehended. Anderson, like Nabokov, understands that distance can increase our understanding of grief, allowing us to see it whole. But distance does not—ought not—necessarily imply a withdrawal. In order to gain sufficient perspective on the pain of exile and the murder of his father, Nabokov did not, in writing Pale Fire, step back from them. He reduced their scale, and let his patience, his precision, his mastery of detail—detail, the god of the model-maker—do the rest. With each of his films, Anderson’s total command of detail—both the physical detail of his sets and costumes, and the emotional detail of the uniformly beautiful performances he elicits from his actors—has enabled him to increase the persuasiveness of his own family Zemblas, without sacrificing any of the paradoxical emotional power that distance affords.
Advertisement
Anderson’s films have frequently been compared to the boxed assemblages of Joseph Cornell, and it’s a useful comparison, as long as one bears in mind that the crucial element, in a Cornell box, is neither the imagery and objects it deploys, nor the Romantic narratives it incorporates and undermines, nor the playfulness and precision with which its objects and narratives have been arranged. The important thing, in a Cornell box, is the box.
Cornell always took pains to construct his boxes himself; indeed the box is the only part of a Cornell work literally “made” by the artist. The box, to Cornell, is a gesture—it draws a boundary around the things it contains, and forces them into a defined relationship, not merely with one another, but with everything outside the box. The box sets out the scale of a ratio; it mediates the halves of a metaphor. It makes explicit, in plain, handcrafted wood and glass, the yearning of a model-maker to analogize the world, and at the same time it frankly emphasizes the limitations, the confines, of his or her ability to do so.
The things in Anderson’s films that recall Cornell’s boxes—the strict, steady, four-square construction of individual shots, by which the cinematic frame becomes a Cornellian gesture, a box drawn around the world of the film, as in Moonrise Kingdom’s dressing room scene, with the little bird-girls framed by strips of light bulbs; the teeming, gridded, curio cabinet sets at the heart of The Life Aquatic, The Darjeeling Limited, and Fantastic Mr. Fox—are often cited as evidence of his work’s “artificiality,” at times with the implication, simple-minded and profoundly mistaken, that a high degree of artifice is somehow inimical to seriousness, to honest emotion, to so-called authenticity. All movies, of course, are equally artificial; it’s just that some are more honest about it than others. In this important sense, the hand-built, model-kit artifice on display behind the pane of an Anderson box is a guarantor of authenticity; indeed I would argue that artifice, openly expressed, is the only true “authenticity” an artist can lay claim to.
Anderson’s films, like the boxes of Cornell or the novels of Nabokov, understand and demonstrate that the magic of art, which renders beauty out of brokenness, disappointment, failure, decay, even ugliness and violence—is authentic only to the degree that it attempts to conceal neither the bleak facts nor the tricks employed in pulling off the presto change-o. It is honest only to the degree that it builds its precise and inescapable box around its maker’s x:y scale version of the world.
“For my next trick,” says Joseph Cornell, or Vladimir Nabokov, or Wes Anderson, “I have put the world into a box.” And when he opens the box, you see something dark and glittering, an orderly mess of shards, refuse, bits of junk and feather and butterfly wing, tokens and totems of memory, maps of exile, documentation of loss. And you say, leaning in, “The world!”
Adapted from the introduction to The Wes Anderson Collection by Matt Zoller Seitz, to be published in October by Abrams Publishers. Copyright © 2013 by Michael Chabon. All rights reserved.